This method mainly based on the results obtained from the AASHTO road test. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k. Aashto rigid pavement design.
Aashto Rigid Pavement Design, About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. The design procedures main objective is to determine the thickness of the concrete slab that will be adequate to carry the projected traffic load for the design period. AASHTO DESIGN Traffic ESALs or E-18s The number and weight of all axle loads from the anticipated vehicles expected during the pavement design life - expressed in 18-kip 80 kN Equivalent Single Axle Loads for each type of pavement.
 5 Design Chart For Rigid Pavement Segment 1 Source Aashto Guide 1993 Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
5 Design Chart For Rigid Pavement Segment 1 Source Aashto Guide 1993 Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Cut across the E SB Cut across M R to the TL Vertically meet other line Read k-value k600pci Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1219 If bedrock. B AASHTO c c1998. However design procedure also provides the amount of steel reinforcement when used as. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
Rigid Pavement Design Anchor.
For the example design scenario a 30-year design life is specified. Higher SN means stronger pavement thus the impact of traffic on pavement deteriorations is less. Condition of pavements are rated with a present. For the example design scenario a 30-year design life is specified. Based on Figure 36 in the 1993 AASHTO Guide for Design of Pavement Structures a Loss of Support 10 results in k eff 250. UFC design method - Calculate the required thickness of rigidconcrete pavement over modifiedstabilized subgrade.
Read another article:
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
7 Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart Source Aashto 1993 Download Scientific Diagram Performance criteria serviceability indexes. Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart Source. Based on Figure 36 in the 1993 AASHTO Guide for Design of Pavement Structures a Loss of Support 10 results in k eff 250. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k.

2 500 a Includes alternative design procedures that can be used in place of or in conjunction with Part II Section 32 Rigid pavement design and. The CivilWeb AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Spreadsheet completes the design of concrete roads or pavements in accordance with AASHTO 1998. Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1218 312 Pavement With Subbase cont Example. This revised manual provides an overview of the methodology termed mechanistic-empirical or M-E pavement design.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Flexible Pavement Thickness Design Aashto Method Source Chapter Use the 1993 AASHTO Empirical Equation Using the previously calculated ESAL results and the 1993 AASHTO empirical rigid pavement design equation the following pavement thickness designs can be calculated. Rigid Pavement Design Manual Revised. Condition of pavements are rated with a present. Use the 1993 AASHTO Empirical Equation Using the previously calculated ESAL results and the 1993 AASHTO empirical rigid pavement design equation the following pavement thickness designs can be calculated.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
5 Design Chart For Rigid Pavement Segment 1 Source Aashto Guide 1993 Download Scientific Diagram LTPP DATA ANALYSIS - Phase I. The design procedures main objective is to determine the thickness of the concrete slab that will be adequate to carry the projected traffic load for the design period. Performance criteria serviceability indexes. Condition of pavements are rated with a present serviceability index PSI ranging from 5 perfect condition to 0 impossible to travel.
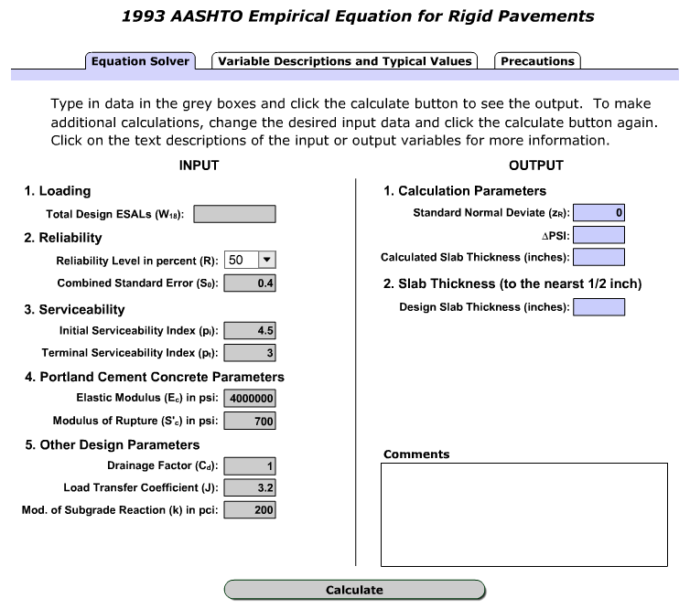 Source: pavementinteractive.org
Source: pavementinteractive.org
1993 Aashto Rigid Pavement Structural Design Pavement Interactive Condition of pavements are rated with a present serviceability index PSI ranging from 5 perfect condition to 0 impossible to travel. Condition of pavements are rated with a present serviceability index PSI ranging from 5 perfect condition to 0 impossible to travel. Rigid ESALs or E -18s Flexible ESALs or E-18s. AASHTO Pavement Thickness Design Guide When designing pavement thickness for flexible and rigid pavements the following considerations should be used.
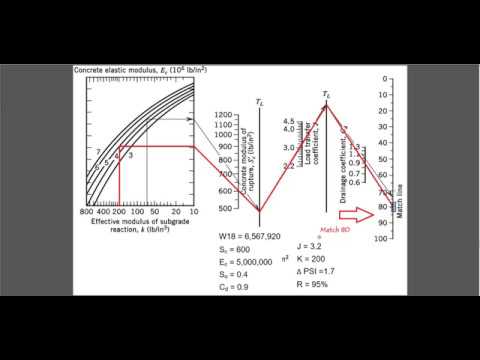 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Design Of Rigid Pavement Using Aashto Method Youtube A Guide for design of pavement structures 246. W 18 189 million ESALs. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Salukitecture Permeable Paving Units Permeable Paving Permeable Permeable Pavers The steps in the 1993 AASHTO rigid pavement design procedure are summarized below in the context of the example baseline scenario presented in Section 621. UFC design method - Calculate the frost penetration depth for flexible and rigidconcrete pavement. Rigid Pavement Design Manual Revised. Subbase thickness10 Subbase modulus30000 psi Subgrade M R10000 psi To get k.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
7 Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart Source Aashto 1993 Download Scientific Diagram Performance criteria serviceability indexes. A Manual of Practice 3rd Edition. However design procedure also provides the amount of steel reinforcement when used as. Cut across the E SB Cut across M R to the TL Vertically meet other line Read k-value k600pci Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1219 If bedrock.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Structural Design Of Highway Flexible Pavement Design Highway Condition of pavements are rated with a present serviceability index PSI ranging from 5 perfect condition to 0 impossible to travel. Condition of pavements are rated with a present serviceability index PSI ranging from 5 perfect condition to 0 impossible to travel. UFC design method - Calculate the frost penetration depth for flexible and rigidconcrete pavement. AASHTO Pavement Thickness Design Guide When designing pavement thickness for flexible and rigid pavements the following considerations should be used.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Design Of Semi Rigid Type Of Flexible Pavements Sciencedirect Download scientific diagram 7. The design procedures main objective is to determine the thickness of the concrete slab that will be adequate to carry the projected traffic load for the design period. Rigid Pavement Design Anchor. 0 a Rigid pavement design rigid pavement joint design 260 a Washington DC.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
5 Design Chart For Rigid Pavement Segment 1 Source Aashto Guide 1993 Download Scientific Diagram 500 a Includes alternative design procedures that can be used in place of or in conjunction with Part II Section 32 Rigid pavement design and. Cut across the E SB Cut across M R to the TL Vertically meet other line Read k-value k600pci Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1219 If bedrock. AASHTO DESIGN Traffic ESALs or E-18s The number and weight of all axle loads from the anticipated vehicles expected during the pavement design life - expressed in 18-kip 80 kN Equivalent Single Axle Loads for each type of pavement. The steps in the 1993 AASHTO rigid pavement design procedure are summarized below in the context of the example baseline scenario presented in Section 621.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Design Of Semi Rigid Type Of Flexible Pavements Sciencedirect Subgrade M R. B ill maps. Performance criteria serviceability indexes. A Manual of Practice 3rd Edition.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
5 Design Chart For Flexible Pavements Using Mean Values For Each Input Download Scientific Diagram Topic 10 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Figure 1218 312 Pavement With Subbase cont Example. For the example design scenario a 30-year design life is specified. This revised manual provides an overview of the methodology termed mechanistic-empirical or M-E pavement design. Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Guide.
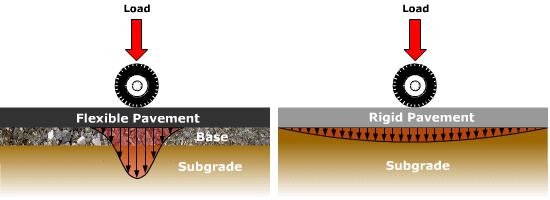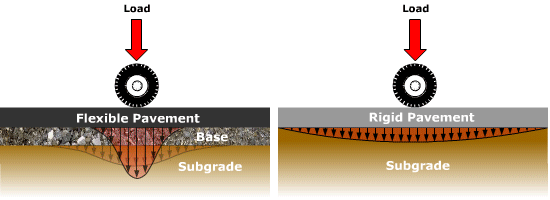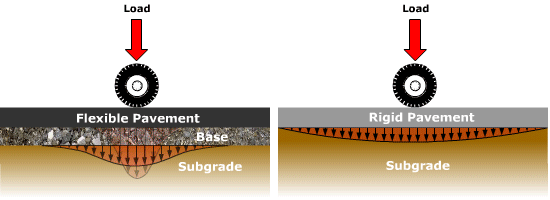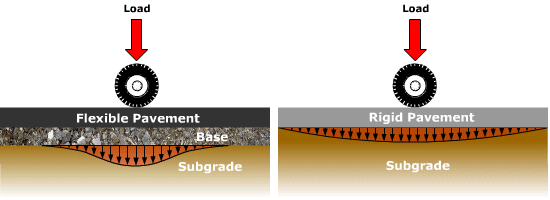 Source: pavementinteractive.org
Source: pavementinteractive.org
Pavement Types Pavement Interactive Where k is in lbin3 and MR is in lbin2. A Manual of Practice 3rd Edition. Determine the analysis period. In the AASHTO flexible pavement design traffic is considered in terms of ESAL for the terminal PSI Table 2013 for p t 25 We must assume the structural number of the pavement.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
6 Design Chart For Rigid Pavement Segment 2 Source Aashto Guide 1993 Download Scientific Diagram This is the design thickness used in other calculations an b Rigid Pavement Design - Based on AASHTO Supplemental Guide Reference. AASHTO Issues Revised Pavement Design Guide. UFC design method - Calculate the frost penetration depth for flexible and rigidconcrete pavement. Where k is in lbin3 and MR is in lbin2.







